The Subramanian committee that was set up to review the matters that led to Kargil war in its detailed report brought out not only the grave deficiencies in India's security management system but it also emphasized that the SECURITY needs have to be consistently analysed as per the changing times. It said ;
“The framework Lord Ismay formulated and Lord Mountbatten recommended was accepted by a national leadership unfamiliar with the intricacies of national security management. There has been very- little change over the past 52 years despite the 1962 debacle, the 1965 stalemate and the 1971 victory, the growing nuclear threat, end of the cold war, continuance of proxy war in Kashmir for over a decade and the revolution in military affairs. The political, bureaucratic, military and intelligence establishments appear to have developed a vested interest in the status quo. National security management recedes into the background in time of peace and is considered too delicate to be tampered with in time of war and proxy war. The Committee strongly feels that the Kargil experience, the continuing proxy war and the prevailing nuclearised security environment justify a thorough review of the national security system in its entirety.
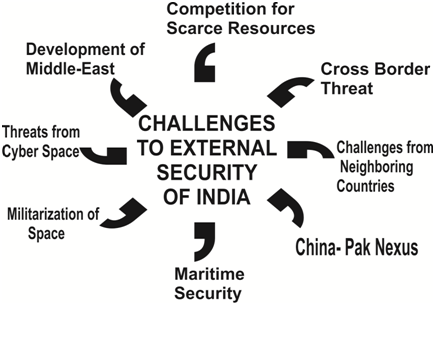
Security, therefore is always circumstantial, situational and has many dimensions, it can only be defined and ensured keeping in view the time and circumstances. Thus the emerging geo-political situation, technological developments, socio-economic environment and numerous other factors have to be carefully analysed before a Nation works out its security needs.
I have, in the succeeding paragraphs therefore, tried to analyse the circumstances, the situations that can have an impact on our security.
1. Globalisation.
When on one end countries are opening up their markets for foreign companies, and every other day one hears of corporate take overs and each country competing to improve its rankings on Ease to do Business Index and rolling out red carpets for the Foreign investors, there is also an increasing threat from some of these companies as they may be working as a front for intelligence gathering. For instance, recently USA blocked almost 37 Chinese companies operating in USA which it believes they were linked to Chinese PLA. Similarly, there are concerns over Chinese involvement in 5G wireless networks, the cellular network equipment sourced from Chinese Company Huawei may contain backdoors enabling surveillance by the Chinese government.. As intelligence sharing, military interoperability increasingly riding on commercial 5G networks, India will also have to take a call soon as 5G has the potential to change the world, it may completely transform the society and the way we do business. Artificial intelligence, communication network platforms are bringing civilian and military futures together. Globalisation has therefore produced a whole new range of threats and risks.
2. Shift in Balance of Power.
The gradual shift in the balance of power from West to the East and USA, the sole superpower, no more interested in acting like a Monitor and prefers to work with Regional powers, has enhanced the competition among the major Regional powers. China meanwhile has systematically got into a position of Power to challenge USA atleast in Asia Pacific. It has armed forces at least numerically many times more than what India possesses. It has also developed its alliances all over in Indian Ocean, Pacific ocean and even as far as Africa and Latin America. It has signed Most Favoured Nation agreements with almost 150 nations. Using its economic clout it has virtually woven a web around India.
3. Importance of IOR and Maritime Security.
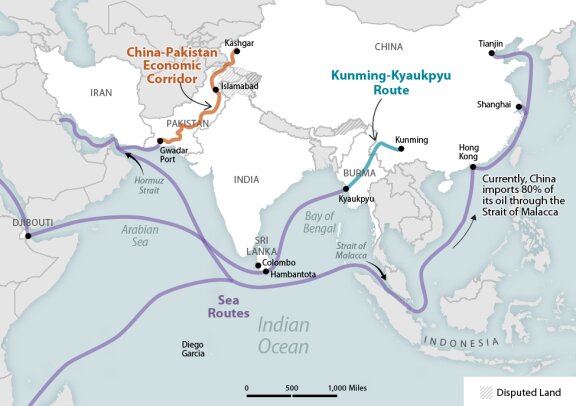
A. All major powers, including United States, India and China have stakes in the security of the IOR(INDIAN OCEAN REGION(. There is a clear shift from Atlantic to Asia – Pacific and in particular Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean has emerged as a center theatre for the challenges of the 21st Century. It provides critical sea trade routes that connect the Middle East, Africa, and South Asia with the broader Asian continent to the East and Europe to the West.
B. Being the world’s busiest trade route - Around 80 percent of the world’s maritime oil trade passes through the IOR. Some 36 million barrels per day – equivalent to about 40 per cent of the world’s oil supply and 64 per cent of oil trade travel through the Indian Ocean, Some most important strategic chokepoints of the world that drives more than 50 per cent of the world’s maritime oil trade are located in this region including Malacca strait, the Bab el Mandeb, Strait of Hormuz.
C. The islands in the Indian Ocean also work significantly to shape security architecture of the IOR. These islands play a vital role along the sea lines of communication (SLOC) by giving easy access to navies continued presence and allowing them to patrol and secure SLOCs during the time of peace and war. Srilanka, Maldives.
D. The rise of China across the maritime region has compelled nations (including India) to reshape their maritime strategies. The tectonic shift in the race for wielding power from the Atlantic Ocean to the Asia-Pacific, more certainly to the Indian Ocean is basically dictated by the economics of it.
E. China,is a bulk importer of Oil that passes through narrow Malacca strait in Indian Ocean. And hence China’s energy security is extremely vulnerable and is hugely dependent upon Indian Ocean sea lanes of communication (SLOCs) that pass through narrow choke points at the northwest and northeast corners. Inorder to offset the vulnerability, China has increased its naval presence in the Indian Ocean in an unprecedented way and China is making huge head way in building a blue water navy. The Chinese navy is emerging as a serious challenger and, therefore, forcing India to re-build its naval power.
F. After its ‘String of Pearls’ strategy through ports development projects in Gwadar, Hambantota, Myanmar and Bangladesh, China is further planning to encircle India by wooing other littoral states in the region. Besides this, China using Its deep pockets, is investing in major infrastructure projects, offering military assistance and political support through its veto power in the UN Security Council to many littoral states. China has secured considerable influence among countries in the Indian Ocean region.
G. In case of Sri Lanka, Chinese Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is roughly five times that of India’s investment. Other island nations like Mauritius and Seychelles are setting new instances of receiving affluent Line of Credits (LoCs) from China. Seychelles and Mauritius are regarded as ideal locations for China as a lot of its oil shipments from the Gulf region and its containers containing manufactured goods destined for Europe and America pass through this region.
H. India as of now is not capable of a ‘containment-cum-counter-encirclement’ policy against China in the Indian Ocean, single handedly. Besides, Indian Navy to be made capable of ensuring India’s strategic interests in the IOR India, has to look for suitable alliances with like-minded nations with similar concerns and values. And hence the importance of Quad, that includes USA, Australia, India and Japan.
I. China is seen as a collective threat to India and the US especially when it is found denouncing the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) in the South China Sea, where China in total disregard to UN Conventions has been carrying out Oil exploration and construction of an air field ; popularly called as Spratly islands.
J. China’s high-speed railways and highways, soon will carry – people and goods to Myanmar’s Bay of Bengal and Pakistan’s Karachi to Greece’s Piraeus and Turkey’s Istanbul. The first-ever railway in Tibet, linking Lhasa with China’s northwest, opened in 2006, may soon reach Kathmandu. Dhaka in Bangladesh and Bandar Abbas in Iran, to India’s east and west respectively, will soon be joined to China by modern rail and road. China would not like to see India usurping this grand vision.
K. China is probably using the same strategy here in South Asia as was used by USA in Latin America. It considered Latin America as its back yard. The U.S. sought to secure its "backyard even if that meant extending support to dictators and despots. From 1870 onward, as the United States emerged as a major world power, the Monroe Doctrine would be used to justify a long series of U.S. interventions in Latin America. So, China, an emerging Superpower is also probably safe guarding its back yard in South Asia, with whatever means possible. It wishes to convey to all; Not A Fly Can Move Without Its Permission In This Region.
L. It would, therefore because of India’s size, its International status, its liberal and democratic society would be wary of it. Viewing from that perspective, China is likely to remain not just a competitor for India but a Rival state, so, this bonhomie with US and Japan and these naval exercises with them in Indian Ocean are going to be viewed as a threat by Chinese to its back yard.
M. This also brings us to a very important concern related to our maritime security. India has a coastline of approx 7500 kms and bulk of India's trade almost 90% in terms of volume and 80% in terms of value takes place through sea. In view of the threat imposed by China, maritime security becomes extremely important.
4. Polarization of the society
A. The rise of fundamentalist forces is posing a serious threat to India’s security. The resurgence of radical political ideologies of mass mobilization, including religious— particularly but not exclusively Islamist—extremism, ethnic fundamentalisms, and Maoism, across wide regions, the emergence of terrorism and its adoption as a tool by both non state actors and a number of state entities to secure political goals is a challenge which every nation is facing today.
B. The democratic institutions are increasingly becoming incapable to effectively manage these ethnic, religion and caste based conflicts in a peaceful manner. The electoral compulsions are compelling the Political organizations to adopt short term policies of appeasement and they are often found short of building consensus and so Violence erupts when conflicting interests cannot be consensually reconciled. The hostile external forces, as a result are able to take advantage of this situation and further aggravate this sense of grievance to such an extent that a small minority are willing to subvert the stability and security of the country. In India, The mushrooming of armed ‘groups’ on Religion, caste and ethnic lines in some parts of the country is a direct consequence of this electoral politics.
C. Given India’s history of communal polarization, partition and violence, Even local demographic transformations can have a significant destabilizing impact. Indian society and politics have yet to become “socially and emotionally secular,” despite constitutional secularism.
5. Corruption.
A. The Police-Bureaucracy- Politician-criminal nexus emboldens the criminal elements. This nexus creates an environment of lawlessness, where influential and rich people violate the law with impunity. This mutually beneficial relationship has seriously impaired the quality of governance in many areas. In fact, the entire criminal justice system is now under strain. Vested interests have developed around these groups with active connivance of corrupt politicians, police officers and civil servants.
B. The militant and extremist forces thrive in this environment. The rise of Left extremism is more due to these compulsions than on ideological grounds.
C. The lawlessness creates a society where the Rich become richer and poor –poorer, the common man suffers due to anarchy and institutions gradually die.
6. Proliferation of Hitech weapon systems.
The proliferation of technological force multipliers and sophisticated weapons and explosives among non-state groups, facilitated by irresponsible, predatory, and rogue states, has made these groups lethal and effective. Consequently the state security system has to be on the lookout 24x7 and got to be lucky each time whereas these groups have to be lucky only once to cause immense damage.
7. Dangerous Environment.
India’s external environment hardly lends itself to stability, and this is validated by the 2020 Fragile State Index, published by Fund for Peace . According to the index, 25 of the 60 states most at risk of failure were located in Asia. Significantly, every country that shares India’s borders is among those countries categorized as High Warning and Alert. Even there is nothing to boast about the internal environment, as India is ranked at 68th in this list almost there with countries like Jordan, Colombia, Bolivia.
South Asia is also the new epicenter of global terror—with “Af-Pak” at its core is the quintessential “bad neighborhood,” arguably one of the most dangerous places on earth, as described by Forbes.
8. Vast and Porous Borders.
India has 15,106 kilometers of land borders and a coastline of about 7,516 kilometers. It shares its Borders with seven countries ; 3400 kms with China and almost the same length with Pakistan. And most of this 15000 kms border is unfenced and open. Besides this, India faces disputed boundaries and competing territorial claims with both Pakistan and China and now Nepal has also entered into the fray. These disputes, particularly with China and Pakistan are not likely to get resolved in foreseeable future and will often be used by these inimical powers to foment trouble in India.
9. Pakistan the eternal enemy.
The animosity that Pakistan has against India and the reasons for it have been discussed so often that it is pointless to discuss any further except that this animosity is likely to continue and India will have to deal with it squarely. Pakistan, is expected to continue to devise newer methods and find newer friends and alliances ; state as well as non-state actors and disgruntled elements within India and outside to target and weaken India. The presence of hostile neighbors, like Pakistan, porous borders enables the disgruntled elements within to get external support, which includes money, arms and sanctuaries. The vested interests exploit these conditions to pursue their own agenda. The break-up of the Indian Union continues to be the main goal of Pakistan’s domestic and foreign policy. The dispute between Pakitan and India , in my opinion can never get resolved because It’s a conflict based on Different Values.
10. Drugs.
With the ‘Golden Crescent’, and the ‘Golden Triangle’ in India’s neighborhood, drug trafficking poses yet another threat to our security. Drug syndicates are generating huge funds, a part of which is being used to give financial support to some of these subversive groups. The intelligence agencies like the ISI are recruiting a number of ‘carriers’ in drug trafficking as their agents. These drug syndicates, agents and subversive groups operating hand in glove have the potential to create grave security threat to the country.
11. India’s Growing Stature.
As India’s economic and military profile grows wider, it would naturally face a range of intrastate and interstate security challenges, which it has to manage. The Energy security to sustain its growth, the security of its sea trading lanes, ports and security of even its allies and friends will have to be thought of. For instance Bhutan is a close ally of India with which India has a security accord, similarly with further growth it will have to bear the responsibility of security of smaller nations to stand firm against Chinese bullying.
12. Emergence of China- Pakistan threat.
A. The strategic partnership between China and Pakistan is now well known and this has created a new threat to India’s security. The relationship is not only about Trade, weapon supplies and infrastructure but it has deepened over the years significantly making the relationship to a strategic geo-political partnership. China using its UN Permanent membership vetoed India’s attempt to declare JEM Chief Masood Azhar as a Global terrorist and it also helped Pakistan convening a special meeting on Kashmir after Indian Govt repealed article 370. China has invested almost $62 billion in its ambitious China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), a set of infrastructure projects linking mainland China with Arabian sea through a port at Gwadar in Pakistan. This allows China to offset any threat to its Energy security through Malacca strait. Chinese troops presence in Gilgit- Baltistan region is again a threat to India’s security.
B. Although China by itself particularly after its experience in Dokhlam and Ladakh may not out rightly attack India because of changed correlation of forces on the ground, but India cannot make a mistake of underestimating the challenge of China's emergence as a formidable power in conventional as well as nuclear capabilities which has resulted in a vast power gap between the two countries. China’s military deployments, infrastructure development along the borders, improved hardware across the three service arms, together, provide the Chinese military with greater offensive capabilities and the ability to make more rapid forward deployments.
C. China has systematically helped Pakistan in building up its armed forces. Pakistan’s MBT and main fighter aircrafts, its missile systems etc all made in China. Courtesy China, Pakistan is today manufacturing indigenously top of the line weapon systems, like Al Khalid tanks, A-100 MRLs etc. India faces a significant nuclear threat from Pakistan and China, between whom a deep connection has historically existed in the nuclear technology and missile delivery domains.
The twin challenge imposed by China and Pakistan compels India to dissipate its resources on two fronts.
13. Strained relations with Neighbors.
India's relations with practically all its neighbours have been strained over a whole range of issues be they of trade, or water sharing or migration or ethnic sensitivities or territorial. At the same time, there have been no even patterns of relationships in the region. India's relations with Bhutan and Maldives have been generally smooth and rancour-free however, with Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka have witnessed significant ups and downs over the years. China using its economic leverage has developed cordial relations with all these neighbours and has been able to finance billions of dollars of projects. China’s presence and pro China govts in these countries hems in India in its own backyard. Srilankan President Rajapakse once during a discussion on the issue of increased China’s role in Srilanka remarked sarcastically ; “Oh! India is like our relative and China is our friend and you know relatives are more stingy than friends.”
14. Urban-Rural Polarization
Despite the slow growth in urban population in India, the urban areas have been poorly managed and this has created new security challenges. Urban vulnerability to political destabilization, terrorism, organized criminal violence, and administrative disorders has been one of the most underestimated aspects of urban development in India. It is significant that the rising proportion of the population in urban centers—projected to rise from 35% in 2020 @ approx. 2.30% annually to 40% by 2030 —will bring more challenges for urban areas. If appropriate measures are not taken regarding better management of urban areas the disorder and mis governance will further increase and may lead to chaos.
15. Environmental degradation.
The environmental degradation is leading us all to all kinds of shortages, pollution and disputes. The sub-national Water Stress Index, formulated by London-based risk analytics firm Verisk Maplecroft, has listed India as the 46th highest risk country in the world. Besides this, What’s more concerning is that 11 of India’s 20 largest cities face an ‘extreme risk’ of water stress and seven are in the ‘high risk’ category. India is categorized as ‘high risk’ in the Climate Change Vulnerability Index, which suggests that effects of climate change like an ‘extended dry season’ would make matters worse for the country’s cities. The World Wide Fund (WWF), in its latest WWF Water Risk Filter report, said that 30 Indian cities face imminent water-related risks unless immediate actions are not taken to mitigate and curb climate change. Climate change may alter the distribution and quality of India’s water resources. These shortages will lead to Interstate disputes related to river water sharing and also cause law and order problems within the cities.
16. Capacity Crunch.
A. This is the biggest challenge that India faces today; Capacity crunch. The kind of challenges that India faces on almost all fronts, ranging from environmental degradation to corruption, terrorism to external threats from difficult neighborhood, India finds itself in a precarious situation as far as resources are concerned.
B. While the availability of central and state forces and organizations for internal & external security management creates an illusion of great strength, the reality is that India faces an acute crisis of capacity. At the qualitative level, political interference and corruption have penetrated every level of police administration—recruitments, appointments, transfers, promotions, and the day-to-day functioning of the police. Millions of cases are lying pending in Indian courts, conviction rates of serious crimes stands abysmally low, The command and control structures of the state police have been deeply compromised, even as communal and caste considerations further undermine the professionalism and effectiveness of the police forces. The result has been a progressive decline—and, in some states, even a collapse—of policing.
C. With a continuous expansion of the theaters of violence and change in model of conflict, these available capacities are already under severe strain, and there is currently little residual surplus. For instance India has been fighting a proxy war in Kashmir for last 30 years, today almost all the Infantry units have had at least served two tenures in Kashmir fighting terrorists and many jawans have had three tenures here as they have in addition served with RR. Besides fighting in Kashmir they have during this period also served in Border areas facing China. This must have surely impacted the overall physical and mental health of our soldier. The Nation cannot afford to fight such protracted wars or else it has to devise newer methods to minimize usage of troops, even if it has to be in a state of war for protracted periods.
D. War is fundamentally a political act. Although, It is the military, that fights, but the decision is taken by the Politicians. Democratic leaders are more likely to avoid difficult situations and decisions because a difficult decision may have adverse political ramifications. Therefore, the fear of losing or decision going awry the fear of reprisal from the domestic constituency compels leaders to bank more on diplomacy, negotiations and persuasiveness. It is precisely this reason as to why Pakistan had been repeatedly targeting us, for last three decades with impunity. However, at the same time, the Govts cannot be seen to be compromising on Borders and terrorism which puts them in a Catch 22 situation. This is what had happened in past and likely to happen in future. The Govt therefore finds itself in a precarious situation because the enemy as well as the Opposition parties are also aware of this weakness of a democratic setup. Thus, democratic leaders have to ensure that ; there is no war or no flaring up of the situation second, there is no compromise and if at all war happens or situation flares up it will not be a destructive one to their support base and they must win. It is a tough call and thus it may compel Govt to take measures which are caused by political expediency rather than military prudence. This emboldens China to trap India as it did in 1962.
E. The twin threat from China and Pakistan has necessitated India to fight a war on five fronts ; Land Borders facing China and Pakistan , space and Seas ; Indian Ocean and Arabian sea. India would need tremendous resources in terms of aircrafts, Submarines, tanks, surveillance equipment etc to deal with this twin threat.
17. Psychological warfare.
A. In medieval times the outcome of the wars was decided on a narrow frontage of few kms and ordinary citizens living in villages and cities had nothing to do with the kings fighting a war, they could go on with their lives unaffected, However, its no more possible now. The wars are fought on thousands of kms of frontage and enemy now can even attack the cities almost 10000 kms inside and can also attack merchant ships in high seas which can bring your entire trade to a halt.
B. Gradually, another dimension, that has got added in the warfare ; psychological warfare. This aimed at influencing the people’s value system, belief system, emotions, motives, reasoning, or behavior. It is used to manipulate attitudes and behaviors favorable to the originator's objectives. This is more dangerous as it can demoralise the whole population and set them against the Govt.
C. Although it originated in WW1 but psychological warfare has gained much more importance in recent years due to the technological advancement in particular, the IT Revolution which has virtually made Geographical boundaries redundant. The Internet facility, social media, and electronic media have all added up a new dimension to the Psy warfare.So, enemy now not only attacks your cities, towns but is also able to attack our minds and manipulate the perception of the citizens.
D. This IT revolution has enabled the enemy to adopt a multi pronged approach to attack the target country’s vitals in all spheres ; diplomatic, political, social and off course military. In such a situation the Social media , the electronic media play an important role in managing the perception of the countrymen. The wars of tomorrow may be won or lost on social media. IT Revolution.
E. The IT revolution and the emergence of social media as a tool to disseminate information and misinformation more quickly, has increased the effectiveness of militant groups, religious fundamentalists and anti-social elements, this has given a fillip to secessionist movements all over the world. it has led to a blurring of the distinction between external and internal threats. Information is power, especially in this Information Age. The media can mould national and international opinion and can be a potent force multiplier both for us as well as the enemy.
F. The recent intrusions by China therefore have to be seen in the right perspective.
It might have served the enemy following objectives ;
I. Dilute the assertive approach of the Indian Govt. By repeated Intrusions.
II. Create doubt in the minds of the people that the Govt is Ineffective and thus dent its political image.
III. weaken the will of the people by showing that we can enter Indian territory anytime and at will. As the IT revolution has made Borders defunct and none can deny its reach, there is an URGENT Need for the Govt to look into this PSY WARFARE impact on the Political stability of the country.
IV. Given the kind of irresponsible Opposition we have which Does not mind conniving with the enemies to settle Political scores, This DIMENSION of warfare is pretty dangerous for the Nation. And it is therefore imperative that Govt acknowledges its long term Effects and takes a serious view of this and prepares a holistic plan to deal with this.
18. Modernization of Armed Forces.
In view of the nature of conflicts, India’s military modernization is by itself a challenge. Given the R&D capabilities and budgetary constraints, the modernization of the Indian defense forces is a complex process as it has to strike a fine balance between manpower and firepower as well as between the acquisition of weapon systems through imports and from indigenous sources. It is this reason why Indian Govt has been relying on short term knee jerk measures and
as a result we have a shortage of Fighter squadrons, submarines, Long range guns and so on.
In short Religious Radicalization, IT Revolution, Inability of Governments to manage social conflicts, close nexus between State and Non state actors, the long porous borders and huge coastline, provide the inimical next door powers ; China and Pakistan enormous opportunities to target India and the budgetary constraints and limited R &D facilities and manufacturing capabilities make the modernization process of armed forces to meet this multidimensional threat extremely difficult and complex. Moreover, as the gap between internal security and external security is blurred managing foreign policy is also an important feature of the security policy.
This is a perilous situation for any Nation to be in and maintain its territorial unity and integrity. The solutions also have to be therefore, worked out only if a Holistic view of the whole situation is taken ranging from economy, foreign policy, intelligence, energy security, border security, demographic patterns, modernization of armed forces, developing manufacturing facilities, R&D and so on.
Here, we will, however, focus our attention only on the armed forces, as to how they can be prepared to meet the emerging security threats to the Nation. If India’s future is to be secured in a planned and ordered manner it is imperative that the armed forces take into account all the security concerns as enumerated above. This places the armed forces once again doing a balancing act in terms of manpower and fire power. It also needs different command structures, tri-service cooperation and capabilities.
One. Armed forces must remain apolitical. As the armed forces keep getting mired in managing internal problems, there is more need to remain apolitical and insular from political insinuations, even at the cost of Political sledging against senior army commanders by political leaders. This has become very imperative when all and sundry have access to social media and there is no regulatory authority managing the contents uploaded on social media. The soldier is more susceptible today to political machinations than he was anytime. Clear cut SOPs must be made and adhered to inorder to keep armed forces professional and apolitical. The Officers at all levels need to be very vigilant and must not allow any dilution of this quintessential value. A little mistake on this count can prove to be disastrous for the country.
Two. Military Doctrine. Our insistence to an extent of being obstinate that India will not attack anyone but always be ready to safe guard its territorial interests had made its response very predictable. It places the inimical powers in an advantageous position who compel us to be always reactive. We need to overcome this defensive mindset. And to do that we need to have our own military doctrine. Military doctrine as widely accepted is defined as the fundamental principles which guide the actions of the armed forces inorder to achieve the national objectives. Hence, inorder to have a military doctrine we need to change the mindset of civilian govts. Armed forces are not defence forces they are the security force which is responsible to provide security to the nation, we need to throw away this defensive mindset. Its only then that we can undertake Pre emptive actions,against the enemy . Had we not been reacting all these years we would have perhaps saved many precious lives and not been subjected to repeated humiliation as it happened during Taj hotel attack. A pre emptive action ensures that the initiative is always with you and active defense implies even if the enemy has taken initiative you have by your actions seized the initiative and thereafter take all measures necessary to retain that initiative. For instance , the moment Pakistan attacked Indian army troops in Uri we carried out a raid across LC and then conducted an air attack on its major terror camp at Balakot, thereafter abolished article 370, virtually trifurcated the state, and made Kashmir a Union territory , the enemy was taken by surprise and is now reacting and dancing to our tune. The same happened, although coincidentally against China in Ladakh where after the initiative was seized at Galwan, we made China to be reactive and seized dominating heights before they could turn the tables, as a result China suffered some more embarrassment.
Three. Intelligence. Although in last few years much has happened on this front but given the kind of threat the Nation faces there is a need to do more. The Kargil crisis of 1999 and Mumbai attack of 2008 had exposed glaring gaps in India’s intelligence capacities and establishments. Besides what the Kargil Committee Report recommended there is also a need for the armed forces to modernize their intelligence gathering system. The Nine SFF units cannot be effectively employed to fight militants/Non state actors within if they are solely dependent on the other intelligence agencies, employing SFF without reliable and real time intelligence like a normal infantry unit would mean gross wastage of the resources. The army must therefore reform its own Field intelligence network in the regions where separatist movements are going on including the naxal infested areas.
Four. Hurting the Inimical Powers where it hurts most.
A. India as discussed is surrounded by inimical powers and is being increasingly challenged by small countries in its own backyard. To overcome this, India will have to make strategy country specific.
B. So far as Pakistan is concerned India will have to raise the cost both for conventional as well as unconventional warfare. The proxy war that apparently proved to be very cost effective option for Pakistan to bleed India, for almost three decades, the diplomatic efforts to isolate Pakistan, the internal strife it is now facing, along with the two surgical strikes, repealing of article 370 and fear of being blacklisted by Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has made this option a little more expensive and riskier. Secondly, India must continue to raise the technological level of its armed forces, thereby making it economically unfeasible for Pakistan to compete even if some of its all-weather friends provide weapon systems at subsidized rates. The more punishment Pakistan continues to get the better chances would be there to keep a control on Pakistan. Thirdly, India must learn to live with this inimical state and must at all costs avoid any TALKS with Pakistan. Any talks with Pakistan legitimises the military dominant system and its support to Terrorists and also at the same time brings back Kashmir on the fore front. A weak, unstable Pakistan is always better for India's security rather than a resurgent Islamic Pakistan.
C. As regards China, India will have to devise a different strategy, it has to identify its Vulnerabilities, and sensitivities and target them, even be it at the geo-political level - Tibet, Taiwan, be it in space, in seas, electro magnetic spectrum and offcourse lets not undermine India’s vibrant Democracy which is not shown in good light in China because of the inherent fears that an authoritative regime will have from its democratic neighbor. Our main aim is to hit back where it hurts most but away from the conflict area so as to avoid escalation. This will put an end to the Pavlonian response while dealing with China.
D. The moment India is seen dealing with these inimical powers sternly the smaller nations in its backyard will also fall in line.
Five. Armed Forces need to become an integral part of a nation’s foreign policy as India grows in stature. Unfortunately, we have failed to learn this lesson and continue to keep the Armed Forces away from the decision making loop but as India grows in stature economically, this can prove to cost us dear if we do not take steps in this direction. The recent example is How Sino –India agreement was signed in 1993 without taking into account Armed forces apprehensions, and ultimately as the events unfolded Dokhlam and Ladakh have proved that armed forces apprehensions were proved to be correct.
Six.
A. Defense manufacturing and acquisition of weapon systems is a complex process and India which is the largest importer of weapon systems despite making huge noises for last 7 decades about indigenization of weapon systems will have to take concrete steps rather than relying on rhetorics.
B. No Nation can ever emerge as a strong player in armament which is weak in manufacturing and thus comes the importance of Make In India and for that many things need to be done ; Land acquisition, Research and Development, Ease to do business, Govt support to Private sector . Unless Make in India becomes a mission that is driven with total resolve by the Govt, India will continue to struggle modernizing its armed forces and at some point of time in future it may have to face problems.
C. A Nation whose institutions produce barely 14-15% engineering graduates who can be gainfully employed, such a task is difficult to be achieved. If at all Govt is serious about Make in India initiative a success it has to bring various stake holders on one platform. It must on immediate basis set up a National Technological University purely for Defense purposes, may be by converting one of the IITs and other complementary institutions and rope in all stake holders on this platform. Lets examine the factors that made Silicon valley a center of innovation.
i). It’s home to 2,000 tech companies, the densest concentration in the world. This provides proximity to suppliers, customers, and cutting-edge research which combiningly gives each a competitive advantage.
ii). The spirit of cooperation. Because many founders of local companies went to school together.
iii). Top-notch universities surround the Silicon Valley. Can we not create a similar thing here in India by setting up a Defense manufacturing Zone with academia (National Technological University), Industry and state working together hand in hand.
Author. Col N Bhatnagar is an alumnus of NDA, Prestigious Def Services Staff College and XLRI. He served in Indian army as an Infantry Officer in all parts of the country and also in Srilanka and has also worked with Reputed Companies - Power, Hospitality and Health Care sector . He has also worked as a National Assesssor of CII for its CII-EXIM Bank Award and HR Excellence award. He has also authored Three Books.
Disclaimer. The views expressed are of Author.